内容概述
- 事件绑定
- 事件流
- 事件对象扩展
- 事件委托
- 事件类型
事件绑定
addEventListener(“eventType”,function(){})1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15<button>按钮</button>
<script>
let btn = document.querySelector("button");
// addEventListener 在同一元素上的同一事件类型添加多个事件,不会被覆盖。
btn.addEventListener("click", function () {
console.log("hello world");
});
btn.addEventListener("click", function () {
console.log("hello script");
});
// 执行结果如下:
// hello world
// hello script
</script>element.onEventType = function(){}1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14<button>按钮</button>
<script>
let btn = document.querySelector("button");
// onEventType 会被下一个同一事件类型的事件覆盖。
btn.onclick = function () {
console.log("hello world");
};
btn.onclick = function () {
console.log("hello script");
};
// 执行结果如下:
// hello script
</script>
两者区别:
addEventListener在同一元素上的同一事件类型添加多个事件,不会被覆盖。addEventListener可以设置元素在捕获阶段触发事件,而onEventType不能。
应用场景:修改别人代码、添加功能的时候用addEventListener会方便很多。
事件流
三个 div 嵌套,都绑定 click 事件,点击最内层的元素,事件如何执行。—— (b).
a:只执行最内层
b:从内到外都执行
c:从外到内都执行
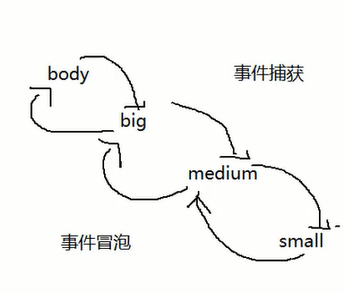
事件捕获与事件冒泡
默认情况下,事件会在冒泡阶段执行。
addEventListener(eventType,fun,boolean);
默认 false:冒泡阶段触发,true:捕获阶段触发。
例 1 - 三个 div 嵌套,都绑定 click 事件,点击最内层的元素。
HTML 代码
1 | <div class="big"> |
CSS 代码
1 | .big { |
在事件冒泡阶段触发。
JS 代码
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17let big = document.querySelector(".big");
let medium = document.querySelector(".medium");
let small = document.querySelector(".small");
big.addEventListener("click", function () {
console.log("Hi,I'm big");
});
medium.addEventListener("click", function () {
console.log("Hi,I'm medium");
});
small.addEventListener("click", function () {
console.log("Hi,I'm small");
});
// 在事件冒泡阶段触发。
// 执行结果如下:
// Hi,I'm small
// Hi,I'm medium
// Hi,I'm big在事件捕获阶段触发。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29let big = document.querySelector(".big");
let medium = document.querySelector(".medium");
let small = document.querySelector(".small");
big.addEventListener(
"click",
function () {
console.log("Hi,I'm big");
},
true
);
medium.addEventListener(
"click",
function () {
console.log("Hi,I'm medium");
},
true
);
small.addEventListener(
"click",
function () {
console.log("Hi,I'm small");
},
true
);
// 在事件捕获阶段触发。
// 执行结果如下:
// Hi,I'm big
// Hi,I'm medium
// Hi,I'm small
事件对象扩展
阻止事件冒泡
e.stopPropagation();
阻止事件冒泡执行。让外层的事件不被执行。
例 1 - 三个 div 嵌套,都绑定 click 事件,点击最内层的元素。
HTML 代码
1 | <div class="big"> |
CSS 代码
1 | .big { |
JS 代码
1 | let big = document.querySelector(".big"); |
例 2 - 点击一个按钮,显示一个容器盒子。点击容器,容器背景颜色改变。点击容器中的按钮,容器隐藏。
HTML 代码
1 | <button class="show">显示</button> |
CSS 代码
1 | .box { |
JS 代码
1 | let show = document.querySelector(`.show`); |
事件默认行为
去掉事件默认行为。
e.preventDefault();return false;
例 1 - 为一个可以跳转到百度的 a 标签设置点击事件。
HTML 代码
1 | <a href="http://www.baidu.com/">baidu</a> |
JS 代码
1 | let a = document.querySelector(`a`); |
以上内容编写于 2021 年 9 月 9 日 01 点 29 分。
事件委托
通过e.target 将子元素的事件委托给父级处理。
例 1 - 实现一个水果列表,让后添加的元素也可以被删除。
HTML 代码
1 | <input type="text" name="" id="" /> |
JS 代码
1 | let btn = document.querySelector("button"); |
事件类型
- 鼠标事件
- 键盘事件
- 触屏事件
键盘事件
e.keyCode
键盘的每个按键都有绑定的键码。
例如,通过以下代码输出不同按键的键码。
1 | document.onkeydown = function (e) { |
例 1 - 通过上下左右键控制元素移动。
偏移量
| 左偏移量 | 上偏移量 | 右偏移量 | 下偏移量 |
|---|---|---|---|
| offsetLeft | offsetTop | offsetRight | offsetDown |
HTML 代码
1 | <div class="box"></div> |
CSS 代码
1 | .box { |
JS 代码
1 | let box = document.querySelector(`.box`); |
触屏事件
1 | let box = document.querySelector(`.box`); |
以上内容编写于 2021 年 9 月 10 日 01 点 20 分。
课后练习
- 实现以下功能(阻止事件冒泡):
- 点击一个按钮,显示一个容器盒子;
- 点击容器,容器背景颜色改变;
- 点击容器中的按钮,容器隐藏。
- 实现一个水果列表,让后添加的元素也可以被删除(事件委托)
- 通过上下左右键控制元素移动。